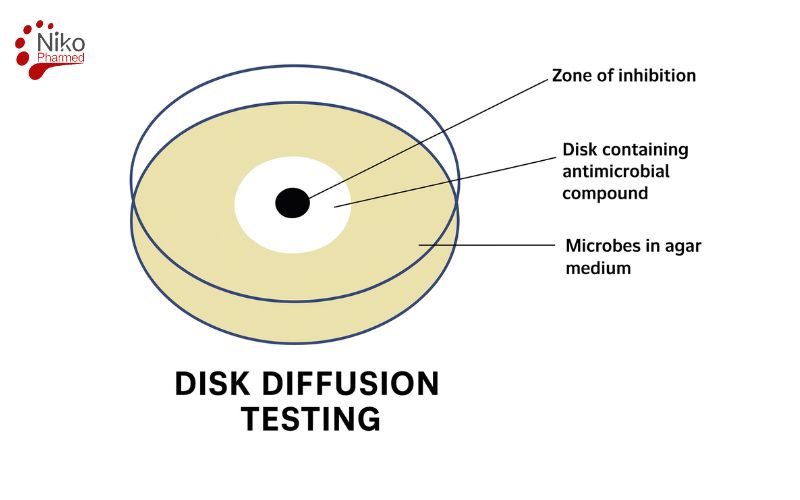
What is Disk Diffusion Testing ?
Disk diffusion testing, also known as the Kirby-Bauer test, is a standardized microbiological method used to evaluate the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents against specific bacterial strains. In this method, a standardized bacterial suspension (typically 0.5 McFarland standard, ≈1.5 × 10⁸ CFU/mL) is uniformly spread onto the surface of a Mueller-Hinton agar plate.
Antibiotic-impregnated paper disks are then placed on the agar surface. During incubation at 35°C for 16–18 hours, the antibiotics diffuse radially from the disks, creating concentration gradients. Bacterial growth is inhibited in zones where the drug concentration exceeds the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for that organism.
The diameter of these clear zones of inhibition is measured in millimeters and compared to standardized interpretive charts provided by organizations like the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). This simple yet powerful test helps guide clinical decisions by determining whether bacteria are susceptible, intermediate, or resistant to specific antibiotics. Disk diffusion is one of Nikopharmad’s core antibacterial testing methods for evaluating the activity of antibiotics against clinically relevant bacteria
Disk Diffusion Testing Procedure
Next, we will examine the process of performing the Disk diffusion testing or Kirby-Bauer test:
Preparation of the Bacterial Inoculum
A pure bacterial colony is selected from a fresh (18–24-hour) culture and suspended in sterile saline or broth. The turbidity of the suspension is adjusted to match the 0.5 McFarland standard, which approximates a bacterial density of 1.5 × 10⁸ CFU/mL. This standard ensures consistency between tests.
Inoculation of the Agar Plate
Using a sterile swab dipped into the standardized inoculum, the bacterial suspension is uniformly spread over the entire surface of a Mueller-Hinton agar plate. This medium is specifically chosen for its:
- Consistent composition and pH (pH 7.2–7.4)
- Support for the growth of non-fastidious organisms
- Ability to allow proper diffusion of antibiotics
The agar depth is standardized at 4 mm to ensure uniform diffusion. Plates are allowed to dry for 3–5 minutes before applying antibiotic disks.
Application of Antibiotic Disks
Commercially prepared paper disks containing fixed concentrations of antibiotics (e.g., 10 µg ampicillin, 30 µg chloramphenicol) are placed on the agar surface using sterile forceps or a disk dispenser. Disks must be placed at least 24 mm apart center-to-center to prevent overlapping zones of inhibition.
Incubation
The inoculated plates are incubated in an inverted position at 35 ± 2°C for 16–18 hours under aerobic conditions. Fastidious organisms may require supplemented media and different incubation conditions (e.g., CO₂ enrichment).
Measurement and Interpretation
After incubation, zones of inhibition—clear areas surrounding the disks where bacterial growth has been prevented—are measured using a ruler or caliper to the nearest millimeter. The diameter of each zone is compared to interpretive criteria published by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST).
For example, according to CLSI guidelines:
- A ≥21 mm zone for ciprofloxacin (5 µg disk) against E. coli indicates susceptibility
- A 16–20 mm zone may indicate intermediate susceptibility
- A ≤15 mm zone suggests resistance
Quality Control
Quality control is critical. Standard strains such as Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 or Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 are tested alongside clinical isolates to ensure disk potency and test accuracy.
Disk diffusion testing provides a qualitative categorization of bacterial susceptibility: Susceptible (S), Intermediate (I), or Resistant (R). This method relies on precise standardization of bacterial inoculum, agar composition, disk potency, and incubation conditions.
When all variables are controlled, the test is a powerful tool for guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy and monitoring resistance trends in bacterial populations.
Why Choose Nikopharmad for Your Disk Diffusion Testing Needs?
ILAC Accreditation & ISO/IEC 17025 Certification
Nikopharmad Laboratory is fully accredited under the ILAC Mutual Recognition Arrangement and certified to ISO/IEC 17025 standards, ensuring that our disk diffusion testing (Kirby-Bauer test) services meet internationally recognized benchmarks for analytical precision, reproducibility, and scientific integrity. Our compliance guarantees reliable results that are accepted by global regulatory bodies and scientific institutions.
Comprehensive Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Services
We provide validated disk diffusion testing based on internationally accepted methodologies, including CLSI M02-A and EUCAST disc diffusion standards. Our services are designed to assess the antimicrobial susceptibility of both clinical pathogens and product-associated isolates using carefully controlled testing conditions—including Mueller-Hinton agar, standardized inoculum preparation (0.5 McFarland), and calibrated antibiotic disks. For fungal pathogens and yeast isolates, we also offer dedicated antifungal activity testing to complement disk diffusion results and build a complete antimicrobial susceptibility profile
Expert Scientific Staff & State-of-the-Art Laboratory Infrastructure
Our disk diffusion testing is conducted by a team of experienced microbiologists, pharmaceutical scientists, and quality assurance specialists. Their deep expertise in antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, clinical microbiology, and regulatory compliance ensures scientifically sound and publication-ready data. Our advanced infrastructure includes automated zone readers, validated reference strains (e.g., E. coli ATCC 25922), and stringent quality control processes.
Rapid Turnaround with Validated Protocols
Nikopharmad’s disk diffusion services are optimized for accelerated timelines without compromising scientific accuracy. Our validated workflows support early-phase product screening, batch release testing, and routine quality control, providing rapid results that align with regulatory and development milestones.
Transparent, Competitive Pricing
We offer cost-effective and flexible pricing models tailored for academic labs, biotech startups, and global pharmaceutical companies alike. Our pricing includes volume discounts, custom panel options, and long-term service agreements, enabling you to manage project budgets without sacrificing quality or compliance.
Data Integrity
Nikopharmad enforces strict data security protocols, including secure electronic record systems and confidentiality agreements (NDAs), to protect client intellectual property. Our documentation is audit-ready and adheres to FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GxP, and global data integrity standards, ensuring confidentiality and regulatory readiness.
Regulatory Compliance & Submission-Ready Reports
All disk diffusion test reports are developed in alignment with CLSI, EUCAST, ISO 20776, and ICH Q6A guidelines. Each report includes detailed test conditions, zone diameter measurements, quality control results, and interpretive breakpoints (Susceptible, Intermediate, Resistant) that meet the requirements of regulatory submissions and clinical development pipelines.
To request testing or a complimentary consultation contact Nikopharmad
Partner with Nikopharmad for Accurate, Compliant, and Efficient Disk Diffusion Testing
By choosing Nikopharmad, you gain a laboratory partner with proven scientific credibility, regulatory-grade quality systems, and a commitment to timely, reliable, and cost-effective results. Our disk diffusion testing ensures your antimicrobial candidates and formulations are evaluated using gold-standard methods—providing the data you need for informed decision-making and regulatory success.
Importance of Disk Diffusion Testing
Guiding Effective Antimicrobial Therapy
The primary importance of disk diffusion testing lies in its ability to help clinicians choose the most effective antibiotic for treating infections. By measuring the zone of inhibition around antibiotic-impregnated disks, laboratories can determine whether a bacterium is:
- Susceptible (S): the antibiotic is likely effective at standard dosages.
- Intermediate (I): the antibiotic may be effective at higher dosages or in certain body sites.
- Resistant (R): the antibiotic is unlikely to be effective.
For example, a zone diameter ≥21 mm for ciprofloxacin (5 µg) against Escherichia coli (CLSI guideline) indicates susceptibility, guiding clinicians to use ciprofloxacin with confidence.
Standardization and Global Use
Disk diffusion is highly standardized and recommended by major bodies like:
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI)
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST)
This standardization ensures:
- Reproducibility: across labs worldwide.
- Comparability: of susceptibility results.
- Reliability: through quality control strains (e.g., E. coli ATCC 25922).
Early Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance
Disk diffusion is essential in detecting resistant strains, such as:
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae
Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Klebsiella pneumoniae
Early identification of resistant bacteria is crucial for:
- Implementing infection control measures
- Modifying treatment regimens
- Preventing hospital outbreaks
Supporting Epidemiological Surveillance
Disk diffusion data contribute to national and international antibiotic resistance surveillance programs, such as:
- WHO’s Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS)
- CDC’s Antibiotic Resistance Threats reports
These data help monitor trends in resistance and guide public health policy and research priorities.
Conclusion
Disk diffusion testing categorizes bacterial susceptibility into three qualitative groups: Susceptible (S), Intermediate (I), or Resistant (R). The accuracy of this method depends on strict standardization of key factors, including the bacterial inoculum density, the composition and depth of the agar medium, the potency of the antibiotic disks, and the incubation conditions. When these variables are properly controlled, the test becomes a reliable tool for selecting effective antibiotic treatments and tracking antimicrobial resistance patterns in bacterial populations.