What is Antifungal Activity Testing?
Antifungal activity testing is a set of standardized laboratory procedures designed to evaluate the efficacy of chemical agents, disinfectants, or bioactive substances against pathogenic or environmental fungi. These assays are critical both for product validation (e.g., disinfectants, hand sanitizers, medical devices) and are often performed alongside antibacterial testing to provide a full efficacy profile.. The testing determines whether a compound exhibits fungistatic (inhibiting fungal growth) or fungicidal (killing fungi) effects, under controlled and reproducible conditions.
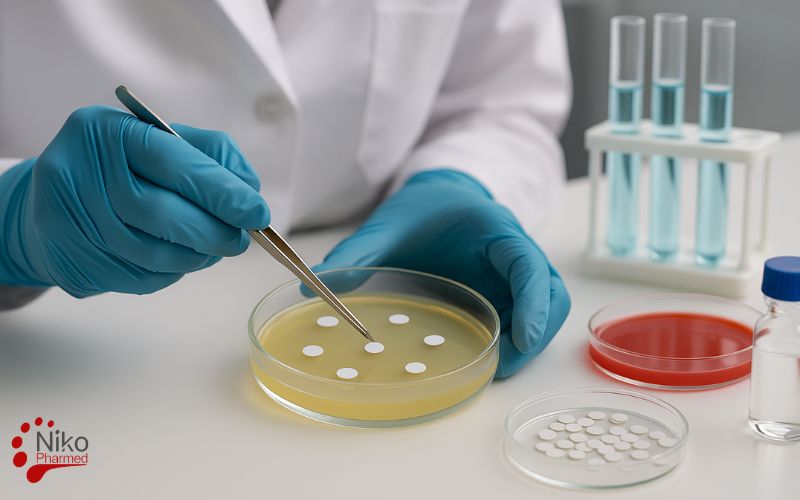
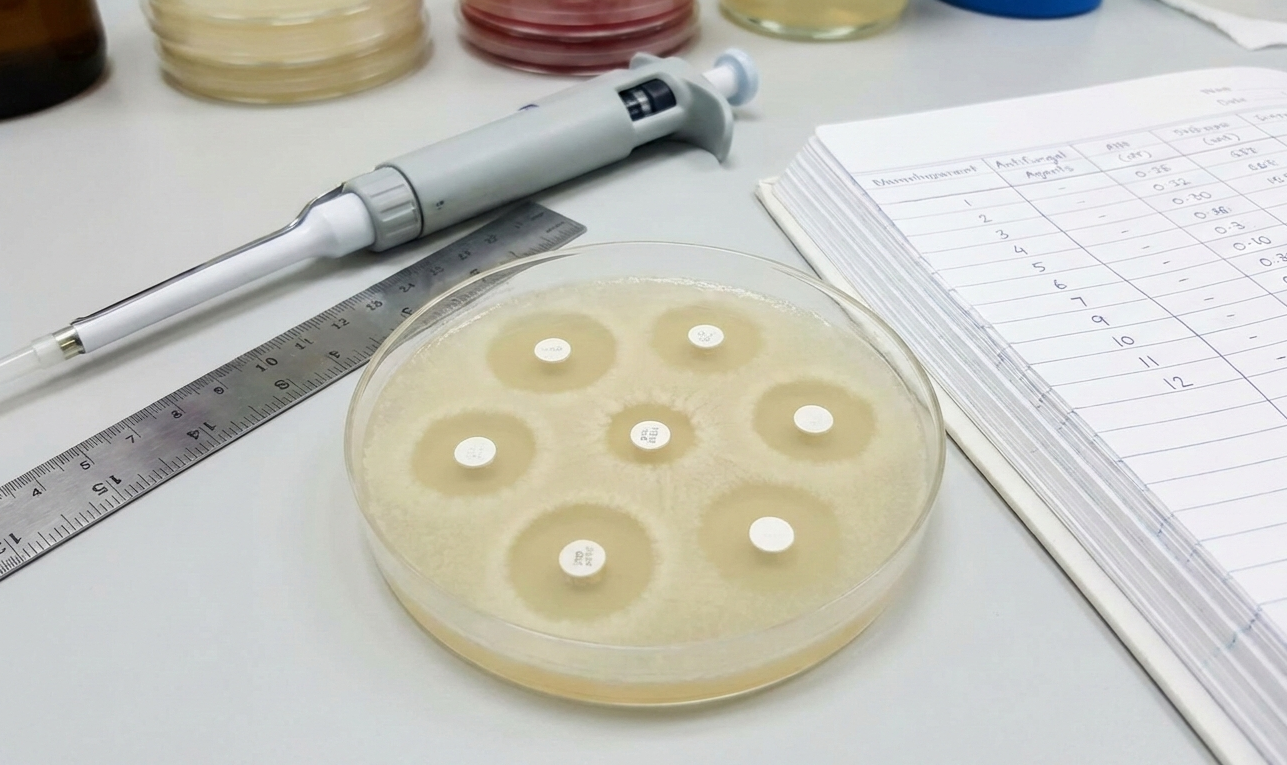
Such testing may involve qualitative methods, such as agar well diffusion or disc diffusion assays to observe zones of inhibition, and quantitative approaches, including determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC), or growth curve analysis.
The choice of method depends on the type of fungi studied yeasts, dermatophytes, or filamentous fungi and the intended application. Ultimately, antifungal susceptibility testing enables researchers to screen and characterize novel bioactive agents, compare their efficacy against standard antifungal drugs, and contribute to understanding their mechanism of action.
To request testing or a complimentary consultation contact Nikopharmad
Antifungal Activity Testing Procedure
In a standard test for antifungals, a known species of fungi such as Candida or Aspergillus is cultured on an appropriate growth medium. A controlled exposure of the test substance to fungus is then achieved in a way mediated by either:
- placing disks or wells bearing the material on the agar plate (zone of inhibition techniques)
- exposing a fungal suspension to varying amounts of the compound in test tubes or microtiter plates (MIC/MFC).
- testing extracts or surfaces of materials that could potentially release antifungal compounds in the future
After incubation, the lab determines either:
- decrease in fungal growth,
- absence or quantity of a clear area (no growth) around the test substance, or
- the lowest concentration of the substance that will not support visible growth (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration – MIC).
These results are subsequently evaluated on the basis of appropriate standards or in-house guidelines in order to determine whether a compound has significant anti-fungal activity.
antifungal susceptibility testing can be applied extensively in:
- pharmaceutical development (anti-fungal drugs, topical preparations)
- medical devices and biomaterials (catheters, wound dressings, coatings
- Cosmetics and personal care (skin, nails, mucous membranes)
However, in the US, as a disinfectants and cleaning agents - food stuffs, agricultural and biotech applications (preservation agents, coating agents, plant
Indeed, a proper antifungal test not only addresses “is it effective or not?” but also “to what extent, at what dose, and on what type of fungus?” This tool is, thus, indispensable in regulatory affairs, correcting claims, and proving non-toxicity and efficacy.
Antifungal Activity Testing Methods
There are a number of standard techniques used in laboratory settings to determine antifungal effectiveness. These techniques depend on the particular commercial product, species, and standards involved in the treatment or prevention of fungal infections.
1. Disk Diffusion (Zone of Inhibition) Method
In this technique, a standardized suspensions of fungi, such as Candida or Aspergillus species, is inoculated on surface of the agar plate. Disks, wells, or spots with the test substances are laid on the surface of the agar plate. The agar plate diffuses for some time, after which the zone free from fungal growth around the disks, termed as the zone of inhibition, is observed.
- The greater the clear zones, the higher the level of antifungal efficacy.
- This technique is commonly employed in screening as well as in making rapid comparisons of different substances.
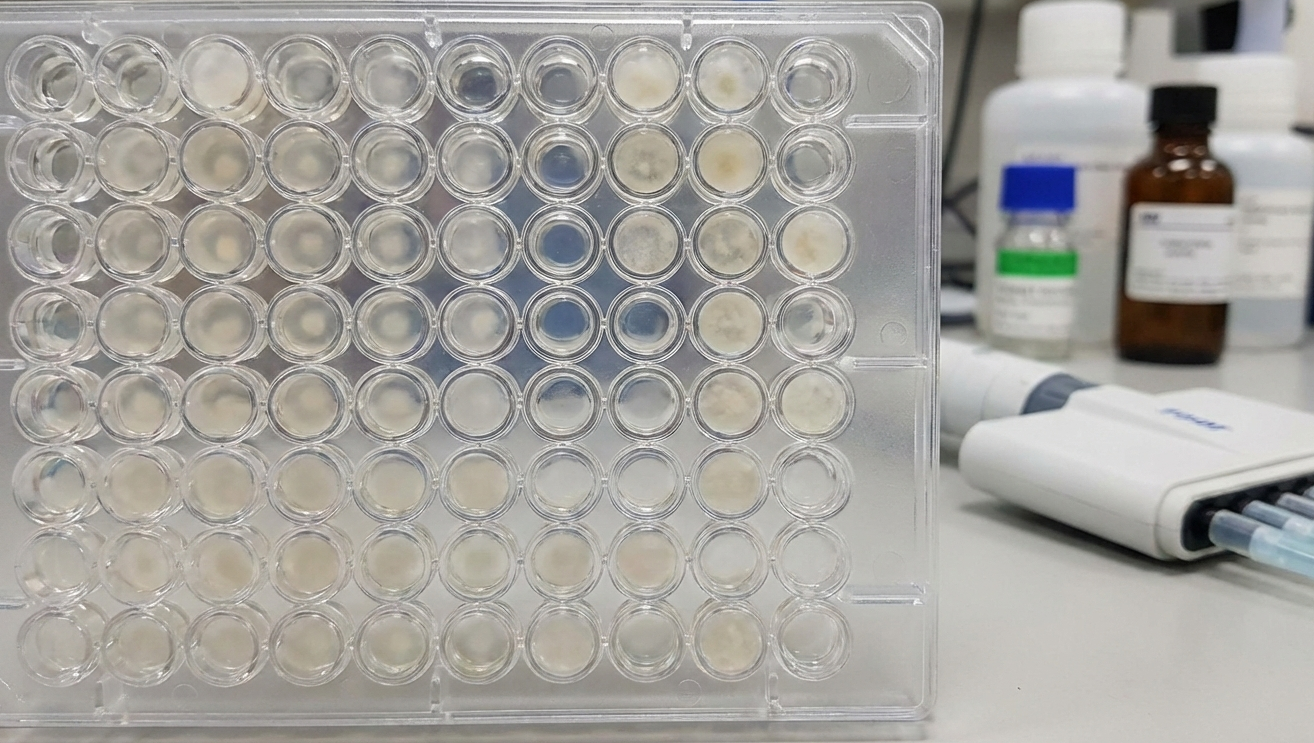
2. Broth Dilution and MIC/MFC
Broth dilution methods are used to determine Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) values, as well as Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC) in some cases.
- The test material is prepared in a liquid growth medium to produce a series of concentrations.
- A standard quantity of fungus is added to the tube or well.
- Following incubation, the concentration at which no visible growth of microorganisms occurs is recorded as the MIC.
- In order to calculate the value of MFC, samples taken from the clear wells can be sub-cultured on agar to determine at what concentration the fungi are actually killed.
This technique can be regarded as more precise and can be applied during the medication production process.
3. Agar Dilution Method
In agar dilution, the test compound is incorporated directly into the agar at varying concentrations before solidification. The agar plates differing in concentrations are inoculated with the fungus.
- Growth or no growth is assessed after incubation.
- This is especially useful if the test involves multiple strains being tested against fewer formulations or pure compounds.
4. Time–Kill Assays (Kinetic Studies)
Time-kill tests are used to measure the speed and level of efficacy of a test agent to reduce fungal growth.
The fungus is challenged by a specific concentration of the testing compound.
At timed intervals (e.g., 0، 2، 4، and 24 hours), samples are removed, diluted, and plated to determine viable fungal colonies.
This test is especially useful in determining the fungistatic and fungicidal effects of antifungals.
5. Surface and Material-Based Antifungal Tests
For medical devices, coatings, textiles, and surfaces that purport to have antifungal action, specific surface tests are applied.
- A fungal suspension would be used to inoculate the material or coupon.
- The remaining viable fungi are then counted after specific times of contact under controlled conditions.
6. Biofilm and Advanced Antifungal Models
In some applications, fungi grow as biofilms rather than free-floating cells. Specialized in vitro models can be used to grow fungal biofilms on relevant materials and then expose them to antifungal agents.
- These models are closer to real-life clinical or industrial conditions and are often used in advanced R&D or for high-risk products.
Antifungal Test Categories and Standards
Nikopharmed Laboratory implements such assays according to international reference standards (DIN EN, ASTM, ISO), ensuring results that are scientifically valid, reproducible, and acceptable for regulatory submissions. The laboratory evaluates antifungal properties of surface disinfectants, general-use chemical disinfectants, medical-use disinfectants, and hand disinfectants, each following specific protocols.
1. Antifungal Property of Surface Disinfectants (Non-Porous Surfaces)
Standards: DIN EN 13697
This standard evaluates the ability of disinfectants to reduce fungal contamination on non-porous surfaces (e.g., stainless steel, glass, ceramics). A known inoculum of fungal spores (commonly Candida albicans or Aspergillus brasiliensis) is applied to the test surface, dried under controlled conditions, and treated with the disinfectant. After exposure, any surviving fungi are recovered and quantified.
Outcome: Logarithmic reduction (e.g., 4-log = 99.99% reduction) is calculated, determining whether the disinfectant achieves the required antifungal efficacy.
2. Antifungal Testing for General Chemical Disinfectants (Public Health Use)
Standards: DIN EN 1650
This suspension test assesses fungicidal activity of disinfectants intended for general public health applications (e.g., floor cleaners, surface sprays). A fungal suspension (standardized inoculum) is mixed with the disinfectant under defined conditions of concentration, contact time, and temperature. After neutralization of the disinfectant, surviving fungi are quantified using plate count methods.
Outcome: Demonstrates fungicidal effectiveness under practical conditions, providing evidence for claims of “fungicidal activity” on product labels.
3. Antifungal Property of Medical Disinfectants
Standards: DIN EN 13624
This test is specific to disinfectants used in medical and healthcare settings (e.g., surgical instruments, hospital surfaces). It measures antifungal efficacy against medically relevant fungi, simulating real clinical environments where infection control is critical. The method follows a suspension-based approach similar to EN 1650, but with stricter parameters and test organisms. Moreover, For medical devices, antifungal evaluations can be integrated into a broader biocompatibility and biological risk assessment strategy according to ISO 10993 and related standards.
Outcome: Ensures disinfectants used in hospitals and clinics are effective against fungal pathogens, thereby reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
4. Antifungal susceptibility testing for Hand Disinfectants
Standards: ASTM E2613, ISO 13624
These tests focus on hand hygiene products, such as alcohol-based hand sanitizers. Volunteers’ hands are artificially contaminated with a standardized fungal suspension, followed by application of the disinfectant under controlled conditions. Surviving fungi are then recovered from the skin and quantified.
Outcome: Provides data on the in vivo antifungal efficacy of hand disinfectants, directly relevant to infection prevention in both clinical and community settings.
Role of Nikopharmed Antifungal Testing Laboratory
Nikopharmed Laboratory conducts these antifungal activity testing services are backed by ISO/IEC 17025 certification and ILAC accreditation with precision instrumentation, trained microbiologists, and in compliance with GLP (Good Laboratory Practice).
To request testing or a complimentary consultation contact Nikopharmad
By applying DIN EN, ASTM, and ISO standards, the laboratory ensures that disinfectants are rigorously evaluated for fungicidal activity across diverse application areas from public health and medical settings to personal hygiene.
This systematic testing enables manufacturers to validate their product claims, meet international regulatory requirements, and ensure public safety by providing disinfectants with proven antifungal efficacy.